|
hsk_libs-dev
163:b63ae088cc97
High Speed Karlsruhe XC878 library collection
|
|
hsk_libs-dev
163:b63ae088cc97
High Speed Karlsruhe XC878 library collection
|
HSK Synchronous Serial Interface headers. More...
#include "hsk_ssc.isr"

Go to the source code of this file.
Macros | |
| #define | SSC_MRST_P05 1 |
| Master mode RX, slave mode TX port P0.5. More... | |
| #define | SSC_MRST_P14 0 |
| Master mode RX, slave mode TX port P1.4. More... | |
| #define | SSC_MRST_P15 2 |
| Master mode RX, slave mode TX port P1.5. More... | |
| #define | SSC_MTSR_P04 (1 << 2) |
| Master mode TX, slave mode RX port P0.4. More... | |
| #define | SSC_MTSR_P13 (0 << 2) |
| Master mode TX, slave mode RX port P1.3. More... | |
| #define | SSC_MTSR_P14 (2 << 2) |
| Master mode TX, slave mode RX port P1.4. More... | |
| #define | SSC_SCLK_P03 (1 << 4) |
| Synchronous clock port P0.3. More... | |
| #define | SSC_SCLK_P12 (0 << 4) |
| Synchronous clock port P1.2. More... | |
| #define | SSC_SCLK_P13 (2 << 4) |
| Synchronous clock port P1.3. More... | |
| #define | SSC_MASTER 1 |
| Master mode, output shift clock on SCLK. More... | |
| #define | SSC_SLAVE 0 |
| Slave mode, receive shift clock on SCLK. More... | |
| #define | SSC_BAUD(bps) (uword)(12000000ul / (bps) - 1) |
| Converts a baud rate value in bits/s into a baud rate value for the hsk_ssc_init() function. More... | |
| #define | SSC_CONF(width, heading, phase, polarity, duplex) (((width) - 1) | ((heading) << 4) | ((phase) << 5) | ((polarity) << 6) | ((duplex) << 7)) |
| Generates an SSC configuration byte. More... | |
| #define | hsk_ssc_busy() ESSC |
| Returns whether the SSC is currently busy with data transmission. More... | |
Functions | |
| void | hsk_ssc_init (const uword baud, const ubyte config, const bool mode) |
| The maximum baud rate in master mode is 12000000 bits/s, and 6000000 bits/s in slave mode. More... | |
| void | hsk_ssc_ports (const ubyte ports) |
| Configure the I/O ports of the SSC unit. More... | |
| void | hsk_ssc_talk (char *buffer, ubyte len) |
| Send and receive data. More... | |
| void | hsk_ssc_enable () |
| Turn the SSC module on. More... | |
| void | hsk_ssc_disable () |
| Turn the SSC module off. More... | |
HSK Synchronous Serial Interface headers.
General purpose serial communication, setup in the following order:
Communication is established by the hsk_ssc_talk() function. Use hsk_ssc_busy() to detect whether a buffer was completely read and written.
For half duplex operation TX and RX pins need to be short circuited.
The TX pin is set up in open drain mode, i.e. an external pull-up resistor is required.
The TX pin needs to be manually configured before calling hsk_ssc_talk() in order to speak or listen on the bus. To listen the TX pin needs to be configured as an input pin, to speak on the bus as an output pin. For efficiency reasons this is not handled by this library (it would result in lots of runtime logic for what should be a single instruction).
Instead it is recommended to define macros in a central header. E.g. for the port configuration SSC_MRST_P05 in slave mode the following code would work:
Syntactically it can be used like a regular function:
| #define hsk_ssc_busy | ( | ) | ESSC |
Returns whether the SSC is currently busy with data transmission.
| #define SSC_BAUD | ( | bps | ) | (uword)(12000000ul / (bps) - 1) |
Converts a baud rate value in bits/s into a baud rate value for the hsk_ssc_init() function.
The distance between adjustable baud rates grows exponentially. Available baud rates in kBit progress like this:
![\[\{12000, 6000, 4000, 3000, 2400, 2000, ...\}\]](form_24.png)
Use the following formula to determine the baud rate that results from a desired value:
![\[{realBps}(bps) = \frac{12000000}{\lfloor\frac{12000000}{bps}\rfloor}\]](form_25.png)
| bps | The desired number in bits/s |
| #define SSC_CONF | ( | width, | |
| heading, | |||
| phase, | |||
| polarity, | |||
| duplex | |||
| ) | (((width) - 1) | ((heading) << 4) | ((phase) << 5) | ((polarity) << 6) | ((duplex) << 7)) |
Generates an SSC configuration byte.
For details check the XC878 user manual section 12.3.5.1.
| width | The data with in bits, the available range is ![$[2;8]$](form_26.png) |
| heading | Use 0 for transmitting/receiving LSB first, 1 for MSB first |
| phase | Use 0 to shift on leading and latch on trailing edge, use 1 to shift on trailing and latch on leading edge |
| polarity | Use 0 for low idle clock, and 1 for high idle clock |
| duplex | Use 0 for full duplex mode and 1 for half duplex |
| #define SSC_MASTER 1 |
Master mode, output shift clock on SCLK.
| #define SSC_SLAVE 0 |
Slave mode, receive shift clock on SCLK.
| void hsk_ssc_disable | ( | ) |
Turn the SSC module off.
| void hsk_ssc_enable | ( | ) |
Turn the SSC module on.
| void hsk_ssc_init | ( | const uword | baud, |
| const ubyte | config, | ||
| const bool | mode | ||
| ) |
The maximum baud rate in master mode is 12000000 bits/s, and 6000000 bits/s in slave mode.
Calling this function turns the SSC off until hsk_ssc_enable() is called.
| void hsk_ssc_ports | ( | const ubyte | ports | ) |
Configure the I/O ports of the SSC unit.
| ports | Selects an SSC I/O Ports I/O port configuration |
| void hsk_ssc_talk | ( | char * | buffer, |
| ubyte | len | ||
| ) |
Send and receive data.
The buffer with the given length should contain the data to transceive and will be filled with the received data upon completion.
The provided buffer needs to reside in xdata memory, e.g. to create and use a string buffer the following should work:
Note that char must not be const and that 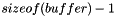 is used to prevent sending and overwriting the terminal 0 character. There may be cases where a terminal 0 character is desired.
is used to prevent sending and overwriting the terminal 0 character. There may be cases where a terminal 0 character is desired.
| buffer | The rx/tx transmission buffer |
| len | The length of the buffer |