|
hsk_libs-dev
163:b63ae088cc97
High Speed Karlsruhe XC878 library collection
|
|
hsk_libs-dev
163:b63ae088cc97
High Speed Karlsruhe XC878 library collection
|
HSK Controller Area Network implementation. More...
Macros | |
| #define | BIT_RWEN 0 |
| CAN_ADCON Read/Write Enable bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_BSY 1 |
| CAN_ADCON Data Transmission Busy bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_AUAD 2 |
| CAN_ADCON Auto Increment/Decrement the Address bits. More... | |
| #define | AUAD_OFF (0 << BIT_AUAD) |
| AUAD auto increment off setting. More... | |
| #define | AUAD_INC1 (1 << BIT_AUAD) |
| AUAD auto increment setting. More... | |
| #define | AUAD_DEC1 (2 << BIT_AUAD) |
| AUAD auto decrement setting. More... | |
| #define | AUAD_INC8 (3 << BIT_AUAD) |
| AUAD auto increment setting. More... | |
| #define | BIT_DATA 4 |
| CAN_ADCON CAN Data Valid bits. More... | |
| #define | CNT_DATA 4 |
| DATA bit count. More... | |
| #define | CAN_AD_WRITE(msk) CAN_ADCON = (1 << BIT_RWEN) | ((msk) << BIT_DATA) |
| Sets up the CAN_AD bus for writing. More... | |
| #define | CAN_AD_READ() CAN_ADCON = 0 |
| Sets up the CAN_AD bus for reading. More... | |
| #define | CAN_AD_READY() while (CAN_ADCON & (1 << BIT_BSY)) |
| Make sure the last read/write has completed. More... | |
| #define | BIT_FCCFG 4 |
| CMCON MultiCAN Clock Configuration bit. More... | |
| #define | OFF_LISTm 0 |
| The ld() of the List Register (LISTm) m offset factor. More... | |
| #define | OFF_MSIDk 0 |
| The ld() of the Message Index Register k offset factor. More... | |
| #define | OFF_MSPNDk 0 |
| The ld() of the Message Pending Register k offset factor. More... | |
| #define | OFF_NODEx 6 |
| The ld() of the Node Register x offset factor. More... | |
| #define | OFF_MOn 3 |
| The ld() of the Message Object n offset factor. More... | |
| #define | NCRx 0x0080 |
| Node x Control Register base address. More... | |
| #define | NSRx 0x0081 |
| Node x Status Register base address. More... | |
| #define | NIPRx 0x0082 |
| Node x Interrupt Pointer Register base address. More... | |
| #define | NPCRx 0x0083 |
| Node x Port Control Register base address. More... | |
| #define | NBTRx 0x0084 |
| Node x Bit Timing Register base address. More... | |
| #define | NECNTx 0x0085 |
| Node x Error Counter Register base address. More... | |
| #define | NFCRx 0x0086 |
| Node x Frame Counter Register base address. More... | |
| #define | BIT_INIT 0 |
| CAN NCRx Node Initialization bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_TRIE 1 |
| CAN NCRx Transfer Interrupt Enable bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_LECIE 2 |
| CAN NCRx LEC Indicated Error Interrupt Enable bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_ALIE 3 |
| CAN NCRx Alert Interrupt Enable bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_CANDIS 4 |
| CAN NCRx CAN Disable. More... | |
| #define | BIT_CCE 6 |
| CAN NCRx Configuration Change Enable bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_CALM 7 |
| CAN NCRx CAN Analyze Mode bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_BRP 0 |
| NBTRx Baud Rate Prescaler bits. More... | |
| #define | BIT_SJW 6 |
| NBTRx (Re) Synchronization Jump Width bits. More... | |
| #define | BIT_TSEG1 8 |
| NBTRx Time Segment Before Sample Point bits. More... | |
| #define | BIT_TSEG2 12 |
| NBTRx Time Segment After Sample Point bits. More... | |
| #define | BIT_DIV8 15 |
| NBTRx Divide Prescaler Clock by 8 bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_RXSEL 0 |
| NPCRx Receive Select bit. More... | |
| #define | CNT_RXSEL 3 |
| RXSEL bit count. More... | |
| #define | PANCTR 0x0071 |
| The Panel Control Register. More... | |
| #define | PANCMD CAN_DATA0 |
| PANCTR Command Register. More... | |
| #define | PANSTATUS CAN_DATA1 |
| PANCTR Status Register. More... | |
| #define | BIT_BUSY 0 |
| PANCTR PANSTATUS Panel Busy Flag bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_RBUSY 1 |
| PANCTR PANSTATUS Result Busy Flag bit. More... | |
| #define | PANAR1 CAN_DATA2 |
| PANCTR Argument 1 Register. More... | |
| #define | PANAR2 CAN_DATA3 |
| PANCTR Argument 2 Register. More... | |
| #define | BIT_ERR 7 |
| PANCTR PANAR2 Error bit. More... | |
| #define | PANCTR_READY() |
| Wait for list operations to complete. More... | |
| #define | PAN_CMD_NOP 0x00 |
| List panel No Operation command. More... | |
| #define | PAN_CMD_INIT 0x01 |
| List panel Initialize Lists command. More... | |
| #define | PAN_CMD_MOVE 0x02 |
| List panel Static Allocate command. More... | |
| #define | PAN_CMD_ALLOC 0x03 |
| List panel Dynamic Allocate command. More... | |
| #define | PAN_CMD_MOVEBEFORE 0x04 |
| List panel Static Insert Before command. More... | |
| #define | PAN_CMD_ALLOCBEFORE 0x05 |
| List panel Dynamic Insert Before command. More... | |
| #define | PAN_CMD_MOVEBEHIND 0x06 |
| List panel Static Insert Behind command. More... | |
| #define | PAN_CMD_ALLOCBEHIND 0x07 |
| List panel Dynamic Insert Behind command. More... | |
| #define | HSK_CAN_MSG_MAX 32 |
| The maximum number of message objects. More... | |
| #define | LIST_UNALLOC 0 |
| This list holds unallocated message objects. More... | |
| #define | LIST_NODEx 1 |
| These lists hold message objects connected to a CAN node. More... | |
| #define | LIST_PENDING 3 |
| This list holds message objects pending assignment to a can node. More... | |
| #define | BIT_CAN_DIS 5 |
| PMCON1 CAN Disable Request bit. More... | |
| #define | MOFCRn 0x0400 |
| Message Object n Function Control Register base address. More... | |
| #define | MOFGPRn 0x0401 |
| Message Object n FIFO/Gateway Pointer Register base address. More... | |
| #define | MOAMRn 0x0403 |
| Message Object n Acceptance Mask Register base address. More... | |
| #define | MODATALn 0x0404 |
| Message Object n Data Register Low base address. More... | |
| #define | MODATAHn 0x0405 |
| Message Object n Data Register High base address. More... | |
| #define | MOARn 0x0406 |
| Message Object n Arbitration Register base address. More... | |
| #define | MOCTRn 0x0407 |
| Message Object n Control Register base address. More... | |
| #define | MOSTATn MOCTRn |
| Message Object n Status Register base address. More... | |
| #define | RESET_DATA CAN_DATA01 |
| The register to write Control Register resets into. More... | |
| #define | SET_DATA CAN_DATA23 |
| The register to write Control Register settings into. More... | |
| #define | RESET 0x3 |
| Bit mask for writing resets. More... | |
| #define | SET 0xC |
| Bit mask for writing settings. More... | |
| #define | BIT_RXPND 0 |
| MOCTRn/MOSTATn Receive Pending bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_TXPND 1 |
| MOCTRn/MOSTATn Transmit Pending bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_RXUPD 2 |
| MOCTRn/MOSTATn Receive Updating bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_NEWDAT 3 |
| MOCTRn/MOSTATn New Data bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_MSGVAL 5 |
| MOCTRn/MOSTATn Message Valid bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_RXEN 7 |
| MOCTRn/MOSTATn Receive Signal Enable bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_TXRQ 8 |
| MOCTRn/MOSTATn Transmit Signal Request bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_TXEN0 9 |
| MOCTRn/MOSTATn Transmit Signal Enable bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_TXEN1 10 |
| MOCTRn/MOSTATn Transmit Signal Enable Select bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_DIR 11 |
| MOCTRn Direction bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_AM 0 |
| MOAMRn Acceptance Mask for Message Identifier bits. More... | |
| #define | CNT_AM 29 |
| AM bit count. More... | |
| #define | BIT_MIDE 29 |
| MOAMRn Acceptance Mask Bit for Message IDE Bit. More... | |
| #define | BIT_DLC 0 |
| MOFCRn Data Length Code bits in byte 3. More... | |
| #define | CNT_DLC 4 |
| DLC bit count. More... | |
| #define | BIT_MMC 0 |
| MOFCRn Message Mode Control bits in byte 0. More... | |
| #define | CNT_MMC 4 |
| MMC bit count. More... | |
| #define | MMC_DEFAULT 0 |
| Regular message mode. More... | |
| #define | MMC_RXBASEFIFO 1 |
| Message is the base of an RX FIFO. More... | |
| #define | MMC_TXBASEFIFO 2 |
| Message is the base of a TX FIFO. More... | |
| #define | MMC_TXSLAVEFIFO 3 |
| Message is a TX FIFO slave. More... | |
| #define | MMC_GATEWAYSRC 4 |
| Message is a source object for a gateway. More... | |
| #define | BIT_IDEXT 0 |
| MOARn Extended CAN Identifier of Message Object n bits. More... | |
| #define | CNT_IDEXT 29 |
| ID bit count. More... | |
| #define | BIT_IDSTD 18 |
| MOARn Standard CAN Identifier of Message Object n bits. More... | |
| #define | CNT_IDSTD 11 |
| ID bit count. More... | |
| #define | BIT_IDE 29 |
| MOARn Identifier Extension Bit of Message Object n. More... | |
| #define | BIT_PRI 30 |
| MOARn Priority Class bits. More... | |
| #define | CNT_PRI 2 |
| PRI bit count. More... | |
| #define | PRI_LIST 1 |
| List order based transmit priority. More... | |
| #define | PRI_ID 2 |
| CAN ID based transmit priority. More... | |
| #define | BIT_LIST 4 |
| MOSTATn List Allocation bits in byte 1. More... | |
| #define | CNT_LIST 4 |
| LIST bit count. More... | |
| #define | MOSTATn_PNEXT CAN_DATA3 |
| MOSTATn Pointer to Next Message Object byte. More... | |
| #define | MOFGPRn_BOT CAN_DATA0 |
| MOFGPRn bottom pointer byte. More... | |
| #define | MOFGPRn_TOP CAN_DATA1 |
| MOFGPRn top pointer byte. More... | |
| #define | MOFGPRn_CUR CAN_DATA2 |
| MOFGPRn current pointer byte. More... | |
| #define | MOFGPRn_SEL CAN_DATA3 |
| MOFGPRn select pointer byte. More... | |
Functions | |
| void | hsk_can_init (const ubyte pins, const ulong baud) |
| Setup CAN communication with the desired baud rate. More... | |
| void | hsk_can_enable (const hsk_can_node node) |
| Go live on the CAN bus. More... | |
| void | hsk_can_disable (const hsk_can_node node) |
| Disable a CAN node. More... | |
| ubyte | hsk_can_status (const hsk_can_node node, const ubyte field) |
| Returns a status field of a CAN node. More... | |
| hsk_can_msg | hsk_can_msg_create (const ulong id, const bool extended, const ubyte dlc) |
| Creates a new CAN message. More... | |
| ubyte | hsk_can_msg_move (const hsk_can_msg msg, const ubyte list) |
| Move the selected message and its slaves to a different list. More... | |
| ubyte | hsk_can_msg_connect (const hsk_can_msg msg, const hsk_can_node node) |
| Connect a message object to a CAN node. More... | |
| ubyte | hsk_can_msg_disconnect (const hsk_can_msg msg) |
| Disconnect a CAN message object from its CAN node. More... | |
| ubyte | hsk_can_msg_delete (const hsk_can_msg msg) |
| Delete a CAN message object. More... | |
| void | hsk_can_msg_getData (const hsk_can_msg msg, ubyte *const msgdata) |
| Gets the current data in the CAN message. More... | |
| void | hsk_can_msg_setData (const hsk_can_msg msg, const ubyte *const msgdata) |
| Sets the current data in the CAN message. More... | |
| void | hsk_can_msg_send (const hsk_can_msg msg) |
| Request transmission of a message. More... | |
| bool | hsk_can_msg_sent (const hsk_can_msg msg) |
| Return whether the message was successfully sent between this and the previous call of this method. More... | |
| void | hsk_can_msg_receive (const hsk_can_msg msg) |
| Return the message into RX mode after sending a message. More... | |
| bool | hsk_can_msg_updated (const hsk_can_msg msg) |
| Return whether the message was updated via CAN bus between this call and the previous call of this method. More... | |
| hsk_can_fifo | hsk_can_fifo_create (ubyte size) |
| Creates a message FIFO. More... | |
| void | hsk_can_fifo_setupRx (hsk_can_fifo fifo, const ulong id, const bool extended, const ubyte dlc) |
| Set the FIFO up for receiving messages. More... | |
| void | hsk_can_fifo_setRxMask (const hsk_can_fifo fifo, ulong msk) |
| Changes the ID matching mask of an RX FIFO. More... | |
| ubyte | hsk_can_fifo_move (hsk_can_fifo fifo, const ubyte list) |
| Move the selected FIFO to a different list. More... | |
| ubyte | hsk_can_fifo_connect (const hsk_can_fifo fifo, const hsk_can_node node) |
| Connect a FIFO to a CAN node. More... | |
| ubyte | hsk_can_fifo_disconnect (const hsk_can_fifo fifo) |
| Disconnect a FIFO from its CAN node. More... | |
| ubyte | hsk_can_fifo_delete (const hsk_can_fifo fifo) |
| Delete a FIFO. More... | |
| void | hsk_can_fifo_next (const hsk_can_fifo fifo) |
| Select the next FIFO entry. More... | |
| bool | hsk_can_fifo_updated (const hsk_can_fifo fifo) |
| Return whether the currently selected FIFO entry was updated via CAN bus between this call and the previous call of this method. More... | |
| void | hsk_can_fifo_getData (const hsk_can_fifo fifo, ubyte *const msgdata) |
| Gets the data from the currently selected FIFO entry. More... | |
| ulong | hsk_can_fifo_getId (const hsk_can_fifo fifo) |
| Returns the CAN ID of the selected FIFO entry. More... | |
| void | hsk_can_data_setIntelSignal (ubyte *const msg, ubyte bitPos, char bitCount, ulong value) |
| Sets a signal value in a data field. More... | |
| void | hsk_can_data_setMotorolaSignal (ubyte *const msg, ubyte bitPos, char bitCount, ulong value) |
| Sets a big endian signal value in a data field. More... | |
| void | hsk_can_data_setSignal (ubyte *const msg, const bool endian, const bool sign, const ubyte bitPos, const char bitCount, const ulong value) |
| Sets a signal value in a data field. More... | |
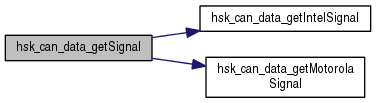
| ulong | hsk_can_data_getIntelSignal (const ubyte *const msg, const bool sign, ubyte bitPos, char bitCount) |
| Get a little endian signal value from a data field. More... | |
| ulong | hsk_can_data_getMotorolaSignal (const ubyte *const msg, const bool sign, ubyte bitPos, char bitCount) |
| Get a big endian signal value from a data field. More... | |
| ulong | hsk_can_data_getSignal (const ubyte *const msg, const bool endian, const bool sign, const ubyte bitPos, const char bitCount) |
| Get a signal value from a data field. More... | |
Variables | |
| bool | hsk_can_initialized = 0 |
| Stores whether common initialization has been performed. More... | |
HSK Controller Area Network implementation.
This file implements the functions defined in hsk_can.h.
The following is a little excursion about CAN on the XC878.
The MultiCAN module is accessible through 3 registers:
| Register | Function | Width |
|---|---|---|
| CAN_ADCON | CAN Address/Data Control Register | 8 bits |
| CAN_AD | CAN Address Register | 16 bits |
| CAN_DATA | CAN Data Register | 32 bits |
These registers give access to a bus. CAN_ADCON is used to control bus (e.g. write or read), everything else is done by writing the desired MultiCAN address into the CAN_AD register. The desired MultiCAN register is then accessible through the CAN_DATA register.
| Register | Representation | Bits | Starting |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAN_ADCON | CAN_ADCON | 8 | 0 |
| CAN_AD | CAN_ADL | 8 | 0 |
| CAN_ADH | 8 | 8 | |
| CAN_ADLH | 16 | 0 | |
| CAN_DATA | CAN_DATA0 | 8 | 0 |
| CAN_DATA1 | 8 | 8 | |
| CAN_DATA2 | 8 | 16 | |
| CAN_DATA3 | 8 | 24 | |
| CAN_DATA01 | 16 | 0 | |
| CAN_DATA23 | 16 | 16 |
Internally the MultiCAN module has register groups, i.e. a structured set of registers that are repeated for each item having the registers. An item may be a node or a list. Each register has a fixed base address and each item a fixed offset. Each register for an item is thus addressed by setting:
The following example points CAN_DATA to the Node 1 Status register:
The MultiCAN module offers 32 message objects that can be linked to one of 8 lists.
List 0 holds the unallocated (i.e. unused) objects. List 1 is connected to CAN node 0. List 2 is connected to CAN node 1.
The following implementation will use 1 of the 5 general purpose lists to park messages.
All the list management will be hidden from the "user".
| #define AUAD_DEC1 (2 << BIT_AUAD) |
AUAD auto decrement setting.
| #define AUAD_INC1 (1 << BIT_AUAD) |
AUAD auto increment setting.
| #define AUAD_INC8 (3 << BIT_AUAD) |
AUAD auto increment setting.
| #define AUAD_OFF (0 << BIT_AUAD) |
AUAD auto increment off setting.
| #define BIT_ALIE 3 |
CAN NCRx Alert Interrupt Enable bit.
| #define BIT_AM 0 |
MOAMRn Acceptance Mask for Message Identifier bits.
| #define BIT_AUAD 2 |
CAN_ADCON Auto Increment/Decrement the Address bits.
| #define BIT_BRP 0 |
NBTRx Baud Rate Prescaler bits.
| #define BIT_BSY 1 |
CAN_ADCON Data Transmission Busy bit.
| #define BIT_BUSY 0 |
PANCTR PANSTATUS Panel Busy Flag bit.
| #define BIT_CALM 7 |
CAN NCRx CAN Analyze Mode bit.
| #define BIT_CAN_DIS 5 |
PMCON1 CAN Disable Request bit.
| #define BIT_CANDIS 4 |
CAN NCRx CAN Disable.
Can be used for a complete shutdown of a CAN node.
| #define BIT_CCE 6 |
CAN NCRx Configuration Change Enable bit.
| #define BIT_DATA 4 |
CAN_ADCON CAN Data Valid bits.
| #define BIT_DIR 11 |
MOCTRn Direction bit.
Set this to 1 for TX, this was figured out by trial and error.
| #define BIT_DIV8 15 |
NBTRx Divide Prescaler Clock by 8 bit.
| #define BIT_DLC 0 |
MOFCRn Data Length Code bits in byte 3.
Valid DLC values range from 0 to 8.
| #define BIT_ERR 7 |
PANCTR PANAR2 Error bit.
| #define BIT_FCCFG 4 |
CMCON MultiCAN Clock Configuration bit.
Used to select PCLK * 2 (1) or PCKL (0) to drive the MultiCAN module.
| #define BIT_IDE 29 |
MOARn Identifier Extension Bit of Message Object n.
| #define BIT_IDEXT 0 |
MOARn Extended CAN Identifier of Message Object n bits.
| #define BIT_IDSTD 18 |
MOARn Standard CAN Identifier of Message Object n bits.
| #define BIT_INIT 0 |
CAN NCRx Node Initialization bit.
| #define BIT_LECIE 2 |
CAN NCRx LEC Indicated Error Interrupt Enable bit.
| #define BIT_LIST 4 |
MOSTATn List Allocation bits in byte 1.
| #define BIT_MIDE 29 |
MOAMRn Acceptance Mask Bit for Message IDE Bit.
| #define BIT_MMC 0 |
MOFCRn Message Mode Control bits in byte 0.
| #define BIT_MSGVAL 5 |
MOCTRn/MOSTATn Message Valid bit.
| #define BIT_NEWDAT 3 |
MOCTRn/MOSTATn New Data bit.
| #define BIT_PRI 30 |
MOARn Priority Class bits.
| #define BIT_RBUSY 1 |
PANCTR PANSTATUS Result Busy Flag bit.
| #define BIT_RWEN 0 |
CAN_ADCON Read/Write Enable bit.
Write is 1.
| #define BIT_RXEN 7 |
MOCTRn/MOSTATn Receive Signal Enable bit.
| #define BIT_RXPND 0 |
MOCTRn/MOSTATn Receive Pending bit.
| #define BIT_RXSEL 0 |
NPCRx Receive Select bit.
| #define BIT_RXUPD 2 |
MOCTRn/MOSTATn Receive Updating bit.
| #define BIT_SJW 6 |
NBTRx (Re) Synchronization Jump Width bits.
| #define BIT_TRIE 1 |
CAN NCRx Transfer Interrupt Enable bit.
| #define BIT_TSEG1 8 |
NBTRx Time Segment Before Sample Point bits.
| #define BIT_TSEG2 12 |
NBTRx Time Segment After Sample Point bits.
| #define BIT_TXEN0 9 |
MOCTRn/MOSTATn Transmit Signal Enable bit.
| #define BIT_TXEN1 10 |
MOCTRn/MOSTATn Transmit Signal Enable Select bit.
| #define BIT_TXPND 1 |
MOCTRn/MOSTATn Transmit Pending bit.
| #define BIT_TXRQ 8 |
MOCTRn/MOSTATn Transmit Signal Request bit.
| #define CAN_AD_READ | ( | ) | CAN_ADCON = 0 |
Sets up the CAN_AD bus for reading.
The controller always reads all 4 data bytes.
| #define CAN_AD_READY | ( | ) | while (CAN_ADCON & (1 << BIT_BSY)) |
Make sure the last read/write has completed.
This is supposed to be mandatory for accessing the data bytes and CAN_ADCON, but tests show that the busy flag is never set if the module runs at 2 times PCLK, which is what this library does.
Sets up the CAN_AD bus for writing.
| msk | A bit mask representing the data bytes that should be written. E.g. 0xC would only write CAN_DATA2 and CAN_DATA3. |
| #define CNT_AM 29 |
AM bit count.
| #define CNT_DATA 4 |
DATA bit count.
| #define CNT_DLC 4 |
DLC bit count.
| #define CNT_IDEXT 29 |
ID bit count.
| #define CNT_IDSTD 11 |
ID bit count.
| #define CNT_LIST 4 |
LIST bit count.
| #define CNT_MMC 4 |
MMC bit count.
| #define CNT_PRI 2 |
PRI bit count.
| #define CNT_RXSEL 3 |
RXSEL bit count.
| #define HSK_CAN_MSG_MAX 32 |
The maximum number of message objects.
| #define LIST_NODEx 1 |
These lists hold message objects connected to a CAN node.
| #define LIST_PENDING 3 |
This list holds message objects pending assignment to a can node.
| #define LIST_UNALLOC 0 |
This list holds unallocated message objects.
| #define MMC_DEFAULT 0 |
Regular message mode.
| #define MMC_GATEWAYSRC 4 |
Message is a source object for a gateway.
| #define MMC_RXBASEFIFO 1 |
Message is the base of an RX FIFO.
| #define MMC_TXBASEFIFO 2 |
Message is the base of a TX FIFO.
| #define MMC_TXSLAVEFIFO 3 |
Message is a TX FIFO slave.
| #define MOAMRn 0x0403 |
Message Object n Acceptance Mask Register base address.
| #define MOARn 0x0406 |
Message Object n Arbitration Register base address.
| #define MOCTRn 0x0407 |
Message Object n Control Register base address.
| #define MODATAHn 0x0405 |
Message Object n Data Register High base address.
| #define MODATALn 0x0404 |
Message Object n Data Register Low base address.
| #define MOFCRn 0x0400 |
Message Object n Function Control Register base address.
| #define MOFGPRn 0x0401 |
Message Object n FIFO/Gateway Pointer Register base address.
| #define MOFGPRn_BOT CAN_DATA0 |
MOFGPRn bottom pointer byte.
| #define MOFGPRn_CUR CAN_DATA2 |
MOFGPRn current pointer byte.
| #define MOFGPRn_SEL CAN_DATA3 |
MOFGPRn select pointer byte.
| #define MOFGPRn_TOP CAN_DATA1 |
MOFGPRn top pointer byte.
| #define MOSTATn MOCTRn |
Message Object n Status Register base address.
The status register is at the same address as the control register. It is accessed by reading from the address instead of writing.
| #define MOSTATn_PNEXT CAN_DATA3 |
MOSTATn Pointer to Next Message Object byte.
| #define NBTRx 0x0084 |
Node x Bit Timing Register base address.
| #define NCRx 0x0080 |
Node x Control Register base address.
| #define NECNTx 0x0085 |
Node x Error Counter Register base address.
| #define NFCRx 0x0086 |
Node x Frame Counter Register base address.
| #define NIPRx 0x0082 |
Node x Interrupt Pointer Register base address.
| #define NPCRx 0x0083 |
Node x Port Control Register base address.
| #define NSRx 0x0081 |
Node x Status Register base address.
| #define OFF_LISTm 0 |
The ld() of the List Register (LISTm) m offset factor.
| #define OFF_MOn 3 |
The ld() of the Message Object n offset factor.
| #define OFF_MSIDk 0 |
The ld() of the Message Index Register k offset factor.
| #define OFF_MSPNDk 0 |
The ld() of the Message Pending Register k offset factor.
| #define OFF_NODEx 6 |
The ld() of the Node Register x offset factor.
| #define PAN_CMD_ALLOC 0x03 |
List panel Dynamic Allocate command.
| #define PAN_CMD_ALLOCBEFORE 0x05 |
List panel Dynamic Insert Before command.
| #define PAN_CMD_ALLOCBEHIND 0x07 |
List panel Dynamic Insert Behind command.
| #define PAN_CMD_INIT 0x01 |
List panel Initialize Lists command.
| #define PAN_CMD_MOVE 0x02 |
List panel Static Allocate command.
| #define PAN_CMD_MOVEBEFORE 0x04 |
List panel Static Insert Before command.
| #define PAN_CMD_MOVEBEHIND 0x06 |
List panel Static Insert Behind command.
| #define PAN_CMD_NOP 0x00 |
List panel No Operation command.
| #define PANAR1 CAN_DATA2 |
PANCTR Argument 1 Register.
| #define PANAR2 CAN_DATA3 |
PANCTR Argument 2 Register.
| #define PANCMD CAN_DATA0 |
PANCTR Command Register.
| #define PANCTR 0x0071 |
The Panel Control Register.
All list manipulations are performed here.
| #define PANCTR_READY | ( | ) |
| #define PANSTATUS CAN_DATA1 |
PANCTR Status Register.
| #define PRI_ID 2 |
CAN ID based transmit priority.
| #define PRI_LIST 1 |
List order based transmit priority.
| #define RESET 0x3 |
Bit mask for writing resets.
| #define RESET_DATA CAN_DATA01 |
The register to write Control Register resets into.
| #define SET 0xC |
Bit mask for writing settings.
| #define SET_DATA CAN_DATA23 |
The register to write Control Register settings into.
|
private |
Get a little endian signal value from a data field.
| msg | The message data field to read from |
| sign | Indicates whether the value has a signed type |
| bitPos | The bit position of the signal |
| bitCount | The length of the signal |
|
private |
Get a big endian signal value from a data field.
| msg | The message data field to read from |
| sign | Indicates whether the value has a signed type |
| bitPos | The bit position of the signal |
| bitCount | The length of the signal |
| ulong hsk_can_data_getSignal | ( | const ubyte *const | msg, |
| const bool | endian, | ||
| const bool | sign, | ||
| const ubyte | bitPos, | ||
| const char | bitCount | ||
| ) |
Get a signal value from a data field.
| msg | The message data field to read from |
| endian | Little or big endian encoding |
| sign | Indicates whether the value has a signed type |
| bitPos | The bit position of the signal |
| bitCount | The length of the signal |
|
private |
Sets a signal value in a data field.
| msg | The message data field to write into |
| bitPos | The bit position of the signal |
| bitCount | The length of the signal |
| value | The signal value to write into the data field |
|
private |
Sets a big endian signal value in a data field.
Big endian signals are bit strange, play with them in the Vector CANdb editor to figure them out.
The start position of a signal is supposed to point to the most significant bit of a signal. Consider a 10 bit message, the bits are indexed:
In that example bit 9 is the most significant bit, bit 0 the least significant. The most significant bit of a signal will be stored in the most significant bits of the message. Under the assumption that the start bit is 2, the message would be stored in the following bits:
Note that the signal spreads to the most significant bits of the next byte. Special care needs to be taken, when mixing little and big endian signals. A 10 bit little endian signal with start bit 2 would cover the following message bits:
| msg | The message data field to write into |
| bitPos | The bit position of the signal |
| bitCount | The length of the signal |
| value | The signal value to write into the data field |
| void hsk_can_data_setSignal | ( | ubyte *const | msg, |
| const bool | endian, | ||
| const bool | sign, | ||
| const ubyte | bitPos, | ||
| const char | bitCount, | ||
| const ulong | value | ||
| ) |
Sets a signal value in a data field.
| msg | The message data field to write into |
| endian | Little or big endian encoding |
| sign | Indicates whether the value has a signed type |
| bitPos | The bit position of the signal |
| bitCount | The length of the signal |
| value | The signal value to write into the data field |
The sign parameter is not required for setting signals, it is just there so that one signal configuration tuple suffices for hsk_can_data_setSignal() and hsk_can_data_getSignal().

| void hsk_can_disable | ( | const hsk_can_node | node | ) |
Disable a CAN node.
This completely shuts down a CAN node, cutting it off from the internal clock, to reduce energy consumption.
| node | The CAN node to disable |
| void hsk_can_enable | ( | const hsk_can_node | node | ) |
Go live on the CAN bus.
To be called when everything is set up.
| node | The CAN node to enable |
| ubyte hsk_can_fifo_connect | ( | const hsk_can_fifo | fifo, |
| const hsk_can_node | node | ||
| ) |
Connect a FIFO to a CAN node.
| fifo | The identifier of the FIFO |
| node | The CAN node to connect to |
| CAN_ERROR | The given FIFO is not valid |
| 0 | Success |
| hsk_can_fifo hsk_can_fifo_create | ( | ubyte | size | ) |
Creates a message FIFO.
FIFOs can be used to ensure that multiplexed signals are not lost.
For receiving multiplexed signals it is recommended to use a FIFO as large as the number of multiplexed messages that might occur in a single burst.
If the multiplexor is large, e.g. 8 bits, it's obviously not possible to carve a 256 messages FIFO out of 32 message objects. Make an educated guess and hope that the signal provider is not hostile.
If the number of available message objects is at least one, but less than the requested length this function succeeds, but the FIFO is only created as long as possible.
| size | The desired FIFO size |
| CAN_ERROR | Creating the FIFO failed |
| [0;32[ | The created FIFO id |
Slave Objects
Slave objects are put into the same list as the base message object, so it can be used as a slave as well.
Always configure slave messages as TXSLAVEs, because in RXMODE the setting is ignored anyway.
Message Pointers
MOFGPRn of the base object holds the message pointers that define the list boundaries. SEL will be used to keep track of where to read/write the next message when interacting with the FIFO.
| ubyte hsk_can_fifo_delete | ( | const hsk_can_fifo | fifo | ) |
Delete a FIFO.
| fifo | The identifier of the FIFO |
| CAN_ERROR | The given FIFO is not valid |
| 0 | Success |
| ubyte hsk_can_fifo_disconnect | ( | const hsk_can_fifo | fifo | ) |
Disconnect a FIFO from its CAN node.
This takes the FIFO out of active communication, without deleting it.
| fifo | The identifier of the FIFO |
| CAN_ERROR | The given FIFO is not valid |
| 0 | Success |

| void hsk_can_fifo_getData | ( | const hsk_can_fifo | fifo, |
| ubyte *const | msgdata | ||
| ) |
Gets the data from the currently selected FIFO entry.
This writes DLC bytes from the FIFO entry into msgdata.
| fifo | The identifier of the FIFO |
| msgdata | The character array to store the message data in |

| ulong hsk_can_fifo_getId | ( | const hsk_can_fifo | fifo | ) |
Returns the CAN ID of the selected FIFO entry.
| fifo | The ID of the FIFO |
|
private |
Move the selected FIFO to a different list.
| fifo | The identifier of the FIFO |
| list | The list to move the FIFO to |
| CAN_ERROR | The given FIFO id is not valid |
| 0 | Move successful |
| void hsk_can_fifo_next | ( | const hsk_can_fifo | fifo | ) |
Select the next FIFO entry.
The hsk_can_fifo_updated() and hsk_can_fifo_getData() functions always refer to a certain message within the FIFO. This function selects the next entry.
| fifo | The ID of the FIFO to select the next entry from |
| void hsk_can_fifo_setRxMask | ( | const hsk_can_fifo | fifo, |
| ulong | msk | ||
| ) |
Changes the ID matching mask of an RX FIFO.
Every RX FIFO is setup to receive only on complete ID matches. This function allows updating the mask.
To generate a mask from a list of IDs use the following formula:
![\[ msk = \sim(id_0 | id_1 | ... | id_n) | (id_0 \& id_1 \& ... \& id_n) \]](form_2.png)
| fifo | The FIFO to change the RX mask for |
| msk | The bit mask to set for the FIFO |
| void hsk_can_fifo_setupRx | ( | hsk_can_fifo | fifo, |
| const ulong | id, | ||
| const bool | extended, | ||
| const ubyte | dlc | ||
| ) |
Set the FIFO up for receiving messages.
| fifo | The FIFO to setup |
| id | The message ID. |
| extended | Set this to 1 for an extended CAN message |
| dlc | The data length code, # of bytes in the message, valid values range from 0 to 8 |
| bool hsk_can_fifo_updated | ( | const hsk_can_fifo | fifo | ) |
Return whether the currently selected FIFO entry was updated via CAN bus between this call and the previous call of this method.
It can be used to decide when to call hsk_can_fifo_getData() and hsk_can_fifo_next().
| fifo | The identifier of the FIFO to check |
| 1 | The FIFO entry was updated since the last call of this function |
| 0 | The FIFO entry has not been updated since the last call of this function |

| void hsk_can_init | ( | const ubyte | pins, |
| const ulong | baud | ||
| ) |
Setup CAN communication with the desired baud rate.
The CAN node is chosen with the pin configuration.
The bus still needs to be enabled after being setup.
| pins | Choose one of 7 CANn_IO_* configurations |
| baud | The target baud rate to use |
Configure the Bit Timing Unit
One bit is s separated into 3 blocks, each of which are multiples of a time quantum. The size of the time quantum (TQ) is controlled by the BRP and DIV8 bits. Because TSYNC is fixed to a single quantum, the other segments should be made up of a minimum of TQs, so TSYNC doesn't get too short (making a bit up of more TQs requires each one to be shorter at the same baud rate). However, the minimum number of TQs is 8 and some spare quantums are needed to adjust the timing between each bit transmission.
| Time Slice | Value | Minimum | Encoding |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSYNC | 1 | Fixed | Implicite |
| TSEG1 | 8 | 3 | 7 |
| TSEG2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| SWJ | 4 | - | 3 |
The above values provide 4 time quantums to adjust between bits without dropping below 8 quantums. The adjustment value is provided with the SWJ time slice.
The sample point is between TSEG1 and TSEG2, i.e. at 75%.
This means one bit requires 12 cycles. The BRP bits can be used to achieve the desired baud rate:
![\[ baud = 48000000 / 12 / BRP \]](form_0.png)
![\[ BRP = 48000000 / 12 / baud \]](form_1.png)
The encoding of BRT is also VALUE+1.
I/O Configuration
There are 7 different I/O pin configurations, four are availabe to node 0 and three to node 1.
| ubyte hsk_can_msg_connect | ( | const hsk_can_msg | msg, |
| const hsk_can_node | node | ||
| ) |
Connect a message object to a CAN node.
| msg | The identifier of the message object |
| node | The CAN node to connect to |
| CAN_ERROR | The given message is not valid |
| 0 | Success |
| hsk_can_msg hsk_can_msg_create | ( | const ulong | id, |
| const bool | extended, | ||
| const ubyte | dlc | ||
| ) |
Creates a new CAN message.
Note that only up to 32 messages can exist at any given time.
Extended messages have 29 bit IDs and non-extended 11 bit IDs.
| id | The message ID. |
| extended | Set this to 1 for an extended CAN message. |
| dlc | The data length code, # of bytes in the message, valid values range from 0 to 8. |
| CAN_ERROR | Creating the message failed |
| [0;32[ | A message identifier |
| ubyte hsk_can_msg_delete | ( | const hsk_can_msg | msg | ) |
Delete a CAN message object.
| msg | The identifier of the message object |
| CAN_ERROR | The given message is not valid |
| 0 | Success |

| ubyte hsk_can_msg_disconnect | ( | const hsk_can_msg | msg | ) |
Disconnect a CAN message object from its CAN node.
This takes a CAN message out of active communication, without deleting it.
| msg | The identifier of the message object |
| CAN_ERROR | The given message is not valid |
| 0 | Success |
| void hsk_can_msg_getData | ( | const hsk_can_msg | msg, |
| ubyte *const | msgdata | ||
| ) |
Gets the current data in the CAN message.
This writes DLC bytes from the CAN message object into msgdata.
| msg | The identifier of the message object |
| msgdata | The character array to store the message data in |
|
private |
Move the selected message and its slaves to a different list.
| msg | The identifier of the message object |
| list | The list to move the message object to |
| CAN_ERROR | The given message object id is not valid |
| 0 | Move successful |
| void hsk_can_msg_receive | ( | const hsk_can_msg | msg | ) |
Return the message into RX mode after sending a message.
After sending a message the messages with the same ID from other bus participants are ignored. This restores the original setting to receive messages.
| msg | The identifier of the message to receive |
| void hsk_can_msg_send | ( | const hsk_can_msg | msg | ) |
Request transmission of a message.
| msg | The identifier of the message to send |
| bool hsk_can_msg_sent | ( | const hsk_can_msg | msg | ) |
Return whether the message was successfully sent between this and the previous call of this method.
| msg | The identifier of the message to check |
| 1 | The message was sent since the last call of this function |
| 0 | The message has not been sent since the last call of this function |
| void hsk_can_msg_setData | ( | const hsk_can_msg | msg, |
| const ubyte *const | msgdata | ||
| ) |
Sets the current data in the CAN message.
This writes DLC bytes from msgdata to the CAN message object.
| msg | The identifier of the message object |
| msgdata | The character array to get the message data from |
| bool hsk_can_msg_updated | ( | const hsk_can_msg | msg | ) |
Return whether the message was updated via CAN bus between this call and the previous call of this method.
An update does not entail a change of message data. It just means the message was received on the CAN bus.
This is useful for cyclic message occurance checks.
| msg | The identifier of the message to check |
| 1 | The message was updated since the last call of this function |
| 0 | The message has not been updated since the last call of this function |
| ubyte hsk_can_status | ( | const hsk_can_node | node, |
| const ubyte | field | ||
| ) |
Returns a status field of a CAN node.
| node | The CAN node to return the status of |
| field | The status field to select |
| bool hsk_can_initialized = 0 |
Stores whether common initialization has been performed.